加密货币:是货币还是泡沫?(上) --科技属性的泡沫
文 | 陈宁迪
自2009年比特币成为第一个去中心化的加密货币以来,10多年间,加密货币的市场蓬勃发展,从比特币一种加密货币发展到全球有成千上万种加密货币,一度市值突破2万亿美元。与此同时,加密货币也从极客(Geek)群体内部的数字游戏,变成了有价格的“商品”,走入了大众的视野。然而绝大部份人对于加密货币的了解仅限于其暴涨暴跌的行情,和道听途说的靠“炒币”实现财富自由的故事。作为金融行业的专业人士,我们不能盲目的相信各类追捧或贬低加密货币的文章,而是需要客观冷静地结合历史,分析加密货币到底是资产还是泡沫。
自2009年比特币成为第一个去中心化的加密货币以来,10多年间,加密货币的市场蓬勃发展,从比特币一种加密货币发展到全球有成千上万种加密货币,一度市值突破2万亿美元。与此同时,加密货币也从极客(Geek)群体内部的数字游戏,变成了有价格的“商品”,走入了大众的视野。然而绝大部份人对于加密货币的了解仅限于其暴涨暴跌的行情,和道听途说的靠“炒币”实现财富自由的故事。作为金融行业的专业人士,我们不能盲目的相信各类追捧或贬低加密货币的文章,而是需要客观冷静地结合历史,分析加密货币到底是资产还是泡沫。
1. 加密货币产生的背景
--金融危机和信任危机

加密货币的概念诞生于2009年,始于比特币的出现,而每每提到加密货币,绕不开的一个概念是区块链。简单概括,我们可以将区块链看作一个网络平台,加密货币通过它进行交易和生成。区块链是去中心化的、防篡改的,通过加密算法保证交易的安全。
加密货币的诞生是数字货币发展到一定阶段的产物。很多人会误将加密货币与数字货币画上等号,事实上,加密货币只是数字货币的一种形式,数字货币中还有一类是虚拟货币,即法定货币的虚拟化和电子化。数字货币的诞生标志着现代支付技术真正开始发展,最早的表现形式是信用卡,到80年代,信用卡在美国社会已经无处不在,它代替了传统的现金、支票、汇款等支付方式,给交易带来了极大的方便,因此也迅速蔓延到其它国家,从此引发了一场无现金支付的革命。

支付技术的下一次迭代是由互联网发起的,高效全球性的互联网交易让数字现金交易达到了新的高度。在早期的互联网上,几乎所有的支付都是通过信用卡进行的。随后,为了提升交易的效率、保证互联网交易的安全性,以及提高交易方之间的信任,互联网本土的支付方案最终出现,第一个获得广泛成功的在线支付公司是2002年上市的Paypal,其后出现的第三方支付公司如支付宝、亚马逊钱包等都属于此列。这一类公司都由政府及银行等大型金融机构监督审查,其管理的虚拟货币实际上是法定货币的虚拟化。
而进入到21世纪,一方面是美国的金融危机及后续的救市方案造成了民众的不信任感,另一方面是互联网支付科技的发展也带来了一些问题,以比特币为代表的加密货币就是在这种大背景下诞生。
美国在2000年经历了互联网泡沫的破裂,通货紧缩,利息降低,大家开始关注信用债及固定收益市场,大量投资互联网的资本也被摧毁。9/11事件发生时,联邦基金利率为3%,事件发生后又加剧了货币宽松政策,利率直接在2002和2003年降到了1%,从而加速了债券证券化市场。理论上此时市场应该会出现通货膨胀,但是互联网及科技产业的发展及应用,以及中国加入WTO的影响使生产效率大幅度提高,成本大大减少,从而抑制了通货膨胀。与此同时,金融机构通过房产证券化,利用CDS (Credit Default Swap,信用违约掉期)等衍生品来赚取巨额利润,资金流向房地产及其相关的金融市场,同时也制造了巨大的金融泡沫。通货膨胀反应到了资产价格和虚拟经济体,并最终到达了难以维持的高度,爆发了2008年的金融危机。为了应对层出不穷的银行倒闭,世界各国的中央银行纷纷出手救助金融机构,印制大量货币,并进行大规模的资产购买操作,这种做法被称为量化宽松。一方面政府和金融机构在金融危机前并未对造成泡沫产生的机构进行有效的监管并放任自流,另一方面危机后为了保住大机构又进行量化宽松,使得民众手里的钱变相贬值,造成大众对政府、银行、华尔街等产生了极大的不信任感,这也是后来一部分人追捧加密货币的原因。
此外,互联网科技的发展使得数字现金交易换取有价商品得到了极大的便利,同时客户通过互联网应用所产生的数据分析也被利用而产生出另一种商品价值。但同样互联网交易的发展和革新也产生了两个问题,其一是被政府集中化监管,对某些国家或者某些产品有交易限制。其二是互联网用户数据价值大量被互联网公司所占用,上述两者所导致用户的隐私和自由等权利被极大的侵犯。比特币及区块链技术的诞生以及其去中心化的本质,理论上可以解决用户之间信任的问题,也可避免了政府银行机构或者大型互联网公司的集中化管理所导致的负面因素。
2. 加密货币是新的泡沫吗?
2. 加密货币是新的泡沫吗?
加密货币的技术基础,是区块链技术,而加密货币也是区块链技术的第一个应用方式,是目前区块链技术工业化最成功最成熟的例子,可以被视为区块链1.0。加密货币的代表比特币,就是用户在一个去中心化的账本上记录交易、产生新的区块后获得的奖励。很多人对加密货币前景的看好来自于对区块链这一技术的信心,将区块链技术称为“下一个互联网”,并延伸出了近年来的“元宇宙”的概念,以及最近火热度极高的虚拟艺术品的NFT(非同质化代币)。
然而从科技发展的历史来看,所有划时代的科技创新在发展初期都会创造一定程度的泡沫。就拿离我们最近的互联网来说,也经历了web1.0、2.0、3.0的阶段,在web1.0向2.0过渡的过程中也发生过美国互联网泡沫的事件。这些泡沫都具备以下特点:1. 可能会是革命性的科技产业,会对未来生活的巨大改变;2. 宽松和低息的货币环境;3. 投资者及消费者对此充满乐观情绪;4. 一浪接一浪对该科技的推崇的文章、出版物和宣传;5. 足够的供给以及可被投资的实体;6. 完全无法用正常的估值体系来评估。
.互联网泡沫的启示
我们回顾一下1995-2000年间的互联网泡沫。1995年,创立仅一年的网景公司(Nascape)上市当日股价就上涨了108%,标志着互联网投资热潮的开端。自此,在欧美、亚洲多个股票市场中,投资者将大量财富投入到价值被高估的高科技公司中,互联网及资讯科技相关企业的股价高速上升。与此同时,1991年以来的低利率环境,为众多互联网初创公司提供了资金。虽然这些公司大部分缺乏实际的营运能力,但由于新颖的“DOT COM”的概念,仍能获得大量投资甚至上市。“DOT COM”公司的商业模式依赖于持续的网络效应,以长期亏损为代价来获得市场份额。在亏损期间,公司依赖于风险资本,尤其是首发股票(所募集的资金)来支付开销。这些股票的新奇性,加上公司实际上亏损且难以估价,把许多股票推上了令人瞠目结舌的高价位。

2000年3月,纳斯达克综合指数攀升到5,048点,较1年前的指数上涨一倍以上,互联网泡沫达到最高点,此后开始破裂。泡沫到2001年消退,大多数网络公司在把风投资金烧光后停止了运营,许多甚至还没有盈利过。而期间曾经叱咤互联网行业的一些公司也走下神坛,股价暴跌,之后被收购甚至倒闭,黯淡退场,其中比较知名的就有Web1.0时代的领军人物,包括网景(Netscape),美国在线(AOL),雅虎等等。
纳斯达克自2003年开始反弹,开启了新一轮的互联网经济和高科技产业的繁荣,但在互联网泡沫破裂后存活下来的巨头,仅剩下苹果及亚马逊两家,而其中亚马逊现有的商业模式也是互联网泡沫以后才慢慢形成而产生新的竞争力的。在2003年开始进入Web2.0 时代后,新成立或重新建立商业模式的公司开始后来居上,现在大家耳熟能详的科技巨头FAANG里的Facebook(现更名为Meta), Netflix(网飞),Google都是泡沫后出现的。
我们可以观察到一个有趣的趋势,历史上所有科技创新浪潮里,剩下的赢家占比基本只有1-2%。真正意义的产业革命都是在泡沫挤破之后才慢慢开始建立的,而最后的产业领导者或者幸存者往往不是一开始的一批进入者,甚至业务模式及应用场景的切入和一开始都存在本质上的不同。因此,对于区块链技术或者加密货币技术来说,最终的赢家可能完全不是我们所能预知的。
.宽松的货币环境刺激泡沫的形成
加密货币市场的疯狂与互联网泡沫的另外一个相似点是货币环境与价格走势的相关性。由下图可以看出,联邦基金利率在1993年为3%,其后一直维持在6%以下,并持续到2000年,同时期内纳斯达克综合指数持续走高,在2000年3月利息升至6%以上后泡沫应声破裂。2002年-2004年联邦基金利率维持在1-2%的低利率区间,互联网行业重新调整,一些企业逐渐恢复元气,另一批新的公司崛起,行业重新洗牌,此后诞生了新的互联网巨头。

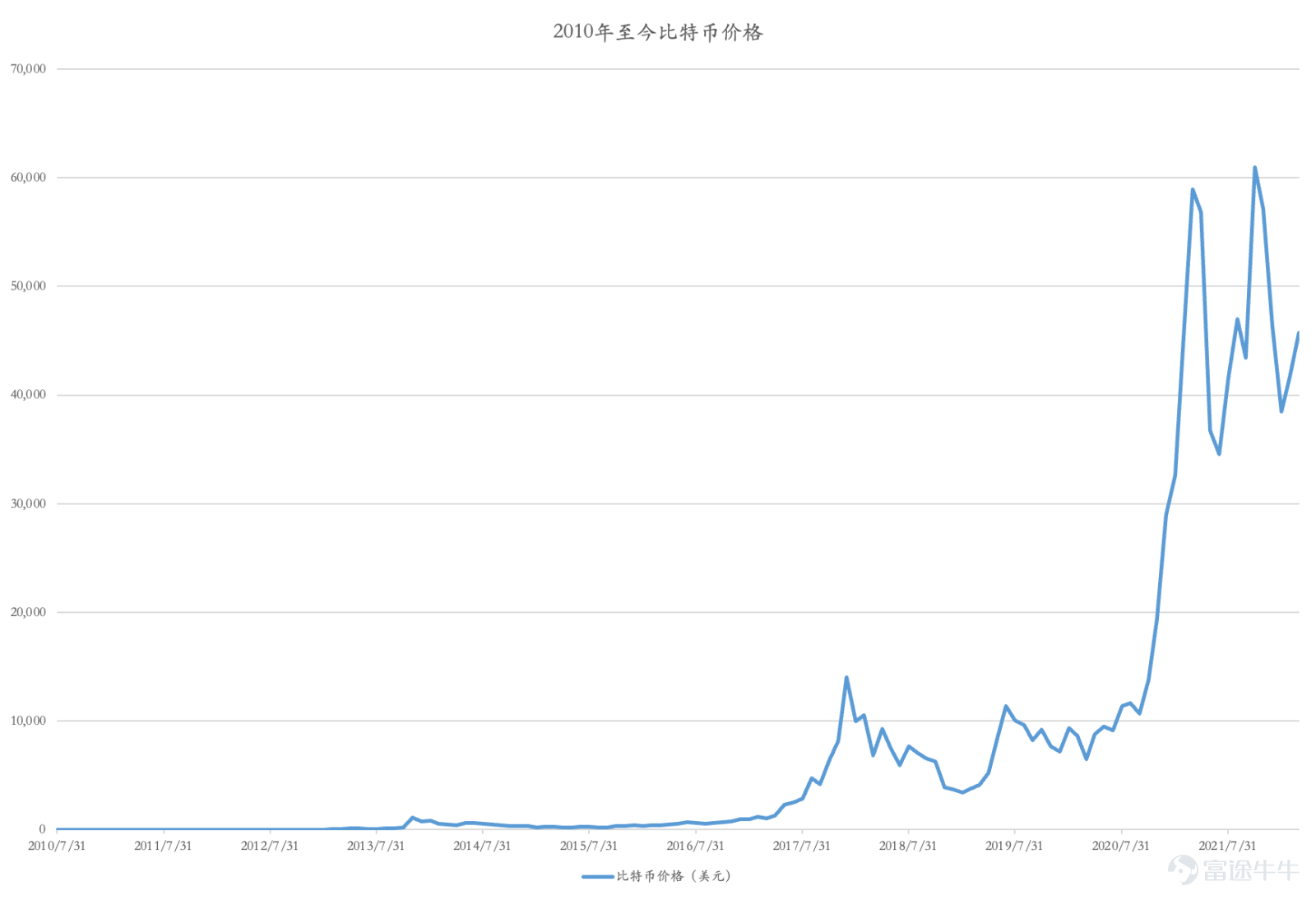
而加密货币诞生于2009年底,2010-2018年间,美联储实行量化宽松,利息一直维持在0.25%,2016年12月美联储开始加息,至2018年12月总计加息八次,基准利率上调至2.5%,2018年整个加密货币崩盘,比特币暴跌80%。而随着2020年疫情开始,美联储又减息并且再次量化宽松,加密货币大幅反弹,屡创新高。

.历史似乎正在重演
加密货币至今的发展与第一代互联网发展,即互联网泡沫,呈现出了很多相同的特点。首先是宽松的货币政策,低利率的环境;其次是部分群体对加密货币技术充满信心,认为其代表着未来,因此也有很多推崇该科技的文章和宣传;第三是高昂的价格,以比特币为例,目前的价格为4万美元一枚,最高时曾经达到6万美元,然而其高昂的价格是缺乏合理内在价值来支撑的,无法用任何一个估值体系对其评估;最后是加密货币的“去中心化”的特征,被认为是有可能会颠覆整个支付行业的,并会在未来取代现有的货币。
下篇文章,我们将从货币的角度来谈加密货币有可能取代现代传统意义的货币吗?
(作者系德林控股1709.HK联合创始人/董事局主席/首席执行官)
风险及免责提示:以上内容仅代表作者个人观点,不代表富途任何立场,亦不构成任何投资建议,富途对此不作任何保证与承诺。
更多信息
评论
登录查看/发表评论